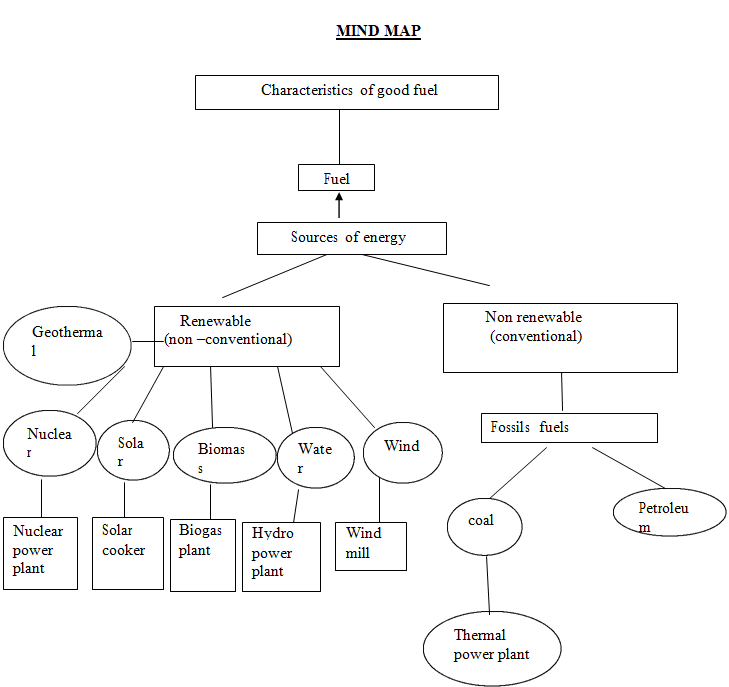
- characteristics of a good fuel:
2. High calorific value
3. Less smoke
4. Easy availability
5. Less residue after burning
6. Inexpensive
7. Easy to store and transport
fossil fuels: were formed millions of years ago, when plants and animal remains got buried under the earth and were subjected to high temperature and pressure conditions. E.g.: Coal, Petroleum, etc.
These fossil fuels are nonrenewable sources of energy and cause environmental problems due to pollution.
Thermal power plants:
(I) Use coal, petroleum, and natural gas to produce thermal electricity. (ii) Electricity transmission is very efficient.
(iii) The steam produced by burning the fossil fuels runs the turbine to produce electricity
hydropower plant:
(i) It is the most conventional renewable energy source obtained from water falling from a great height.
(ii) It is a clean & nonpolluting source of energy.
(iii) Dams are constructed to collect water flowing in high-altitude rivers. The stored water has a lot of potential energy.
(iv) When water is allowed to fall from a height, potential energy changes to kinetic energy, which rotates the turbines to produce electricity.
Disadvantages of Hydro power plant:
(i) Highly expensive to construct.
(ii) Dams cannot be constructed on all river sites.
(iii) Large areas o human habitation and agricultural fields get submerged.
(iv) People face social and environmental problems.
Nonconventional sources:
(1) Biomass:
o It is the source of the conventionally used fuels that are used in our country. E.g.: Cow dung cakes, fire-wood, coal, charcoal
Biogas: It is a mixture of gases produced during the decomposition of biomass in the absence of Oxygen. (Anaerobic Respiration). Methane is the major component of biogas.
Biogas plants: Animal dung, sewage, crop residues, vegetable wastes, poultry droppings, etc. are used to produce Bio gas in Biogas plants.
(2) Wind energy:
It can be converted into mechanical and electrical energy.
Windmill-
Advantages: (i) Eco-friendly (ii) Renewable
Disadvantages: (i) Wind speed is not uniform always.
(ii) Needs a large area to erect a series of windmills.
(iii) A large amount of investment is needed.
(iv) Output is less as compared to investment
(3) Solar energy:
Solar radiation can be converted to electricity through solar cells (photovoltaic cells).
Photovoltaic cells convert solar radiation directly into electricity through silicon solar cells.
Solar cells are arranged on large flat sheets to form a solar panel.
Solar cookers are painted black from the outside and a large glass plate traps solar radiation by the greenhouse effect.
Advantages of Solar cookers:
(i) Eco-friendly
(ii) Renewable
(iii) Used in rural areas.
(iv) Retains all the nutrients in food due to slow cooking. o Disadvantages of solar cooker:
(i) Silicon cells are expensive.
(ii) Solar radiations are not uniform over the earth‘s surface. (iii) Cannot be used at night or on cloudy days.
(iv) Cannot be used to make chapattis for frying as these require a temperature of 1400C or more.
(Maximum temperature of 1000C only can be achieved in a solar cooker)
Other solar devices- Solar water heater, Solar furnace.
(4) Geothermal energy:
(i) Energy harnessed from the heat of the sun is called Geothermal energy.
(ii) Magma is formed when this heat melts the rocks. The molten rocks and hot gases are called magma
(iii) The magma gets collected at some depths below the earth‘s surface. These places are called ‗Hot spots‖
(iv) When underground water comes in contact with these hot spots, it changes into steam, which can be used to generate electricity.
o Advantages of Geothermal energy:
(i) Renewable
(ii Inexpensive
Disadvantages of Geothermal energy:
(i) Only a few sites are available for harnessing energy.
(ii) Expensive
(5) Nuclear energy:
(i) Energy released when some changes take place in the nucleus of the atom of a substance, is called Nuclear energy.
(ii) It is used for heat generation, and fuel for marine vessels.
(i) Alternative source of energy due to depletion of fossil fuels.
(ii) From a small amount of fuel, a large amount of energy is released. o Disadvantages of Nuclear energy:
(i) Risk of nuclear waste leakage
(ii) High cost of setting up of nuclear plant
(iii) Pollution of environment.
(6) Energy from the sea-
(A) Tidal energy: Locations in India – Gulf of Kutch, Gujrat & W. Bengal (i) Depends upon harnessing the rise and fall of sea level due to tidal action.
(ii) Dams are constructed across a narrow part of the sea and the turbine converts tidal energy into electrical energy.
Disadvantages: Uniform tidal action is not seen (B) Wave energy:
(i) Kinetic energy of the waves of the sea are used to rotate turbines.. (ii) These turbines generate electrical energy
Important diagrams-
1. Hydropower plant
2. Biogas plant
3. A windmill
4. A solar cooker
FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I
Q.PAPER
MARKS-30 TIME- 70 MINUTES
Instructions:
· Questions: 1 to 5 – 1 Mark each · Questions: 6 to 9 – 2 Marks each
· Questions: 10 to 13 – 3 Marks each · Questions 14 – 5 Marks
1. Name the component of sunlight, exposure to which may cause skin cancer.
2. Flowing water possesses which type of energy.
3. Name one place in India where a wind energy power station is installed.
4. What is a solar panel?
5. What type of energy transformation takes place during the winding of the spring of a clock?
6. Write two differences between renewable and non–renewable sources of energy.
7. What is the principle of solar cooker? Name two types of solar cookers.
8. Name any two types of harmful nuclear radiation emitted during nuclear fission.
9. What is a thermal power plant? Where it is preferably situated?
10. What is the principle of solar cooker? Give two limitations and two advantages of solar cookers.
11. Name the fuel for the hydropower plant. Mention two advantages and disadvantages of producing electricity at the hydropower plant.
12. Explain why:
a) It is difficult to burn a piece of wood fresh from a tree.
b) Pouring dry sand over the fire extinguishes it.
c) It is difficult to use hydrogen as a source of energy.
13. What are the different types of energies obtained from the sea? Explain.
14. a) What is the principle of Biogas? b) Explain it working in brief.
c) Draw a labeled diagram of biogas.
HOTS QUESTIONS (SOLVED)
1. Name the materials used for making solar cells.
A. Silicon, Germanium and Selenium
2. What fraction of solar energy reaches the earth‘s surface?
A. 47%
3. Name the process that produces a large amount of energy in the sun.
A. Nuclear fusion
4. Why is biogas called a clean fuel?
A. Because it- (i) leaves no ash (ii) does not cause pollution (iii) does not produce any poisonous gas.
HOTS QUESTIONS (UNSOLVED) 1. What is the use of black-painted surfaces in solar heating devices?
2. Why are bio-gas plants considered to be a boon to farmers? Give reason.
3. Hydroelectricity generated at a dam may be considered another form of solar energy. Why? 4. How is the slurry left over after the generation of biogas in the biogas plant used?
5. Why is charcoal considered to be a better fuel than wood?
6. Why a solar cooker cannot be used for frying or making chapattis?
7. In parabolic reflector-type coolers, even temperatures up to 1800C- 2000C can be attained. How?
8. Modern chulahs are more efficient than traditional chulahs. Why? 9. How is hydro energy converted into electrical energy?
10. Explain, why only a part of the solar energy that strikes the upper regions of the atmosphere reaches the surface of the earth.
ENERGY
ORAL QUESTIONS (CONVERSATION TYPE)
1. a) What is a good source of energy?
b) Name one good source of energy.
c) It is a renewable source of energy?
d) Is it a conventional or non – conventional source of energy?
e) What other name is given to it?
f) What is a fossil fuel?
g) Name any other two fossil fuels.
2. a) Which is the ultimate source of all forms of energy?
b) Can you explain?
c) Name some renewable source of energy arising due to the sun.
d) Name some non–renewable source of energy arising due to the sun.
e) Why is the energy contained in fossil fuels considered due to the sun‘s energy?

GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings