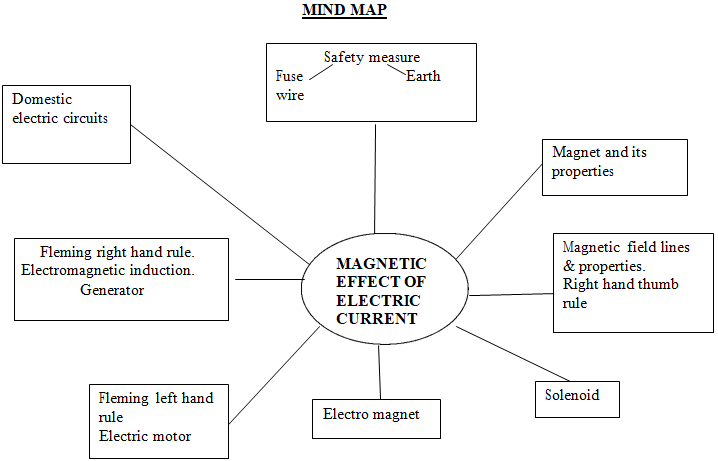
magnet: (i) is an object that attracts objects made of iron, cobalt & nickel. (ii) Comes to rest in a North-South direction, when suspended freely.
magnets are used: (i) In radio & stereo speakers, (ii) In refrigerator doors, (iii) on audio & video cassette players, (iv) On hard discs & floppies of computers & (v) in children‘s toys.
magnetic field: The area around a magnet where a magnetic force is experienced is called a magnetic field. It is a quantity that has both direction & magnitude.
magnetic field lines: A magnetic field is represented by field lines. They are lines drawn in a Magnetic field along which a North magnetic pole moves. Magnetic field lines are called as Magnetic lines of force.
properties of Magnetic field lines:
(i) They do not intersect each other.
(ii) It is taken by convention that magnetic field lines emerge from the North pole and merge at the South pole. Inside the magnet, their direction is from the South pole to the North pole. Therefore magnetic field lines are closed curves.
magnetic field lines due to a current through a straight conductor (wire)- consist of a series of concentric circles whose direction is given by the Right-hand thumb rule.
right-hand thumb rule: If a current-carrying straight conductor is held in your right hand such that the thumb points towards the direction of current, then the wrapped fingers show the direction of magnetic field lines.
magnetic field lines due to a current through a circular loop
The strength of the magnetic field at the centre of the loop(coil)depends on:
(i) The radius of the coil- The strength of the magnetic field is inversely proportional to the radius of the coil. If the radius increases, the magnetic strength at the centre decreases.
(ii) The number of turns in the coil: As the number of turns in the coil increase, the magnetic strength at the centre increases, because the current in each circular turn is having the same direction, thus the field due to each turn adds up.
(iii) The strength of the current flowing in the coil: as the strength of the current increases, the strength of the magnetic fields also increases.
solenoid:
v(i) A coil of many turns of insulated copper wire wrapped in the shape of a cylinder is called a Solenoid.
(ii) The magnetic field produced by a Solenoid is similar to a bar magnet.
(iii) The strength of the magnetic field is proportional to the number of turns & magnitude of the current.
Fleming‘s Left-hand rule: Stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of the left hand such that they are mutually perpendicular. The forefinger points in the direction of the magnetic field and the centre finger in the direction of current, then the thumb gives the direction of force acting on the conductor.
electric motor: A device that converts electric energy to mechanical energy.
principle of an Electric motor: When a rectangular coil is placed in a magnetic field and a current is passed through it, force acts on the coil, which rotates it continuously. With the rotation of the coil, the shaft attached to it also rotates.
electromagnetic induction: Electricity production as a result of magnetism (induced current) is called Electromagnetic induction.
Fleming‘s Right-hand rule: gives the direction of the induced current.
Stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of the right hand such that they are mutually perpendicular. The forefinger points in the direction of the magnetic field and the centre finger in the direction of induced current, then the thumb gives the direction of motion of the conductor.
electric generator: A device that converts mechanical energy to electric energy.
Electric generators is of two types- (i) A.C generator (ii) D. C generator
principle of Electric generator: Electromagnetic induction
domestic electric circuits:
vWe receive electric supply through mains supported through the poles or cables. In our houses, we receive AC electric power of 220V with a frequency of 50Hz.
The 3 wires are as follows- (i) Live wire– (Red insulated, Positive)
(ii) Neutral wire– (Black insulated, Negative)
(iii) Earth wire- (Green insulated) for safety measures to ensure that any leakage of current to a metallic body does not give any serious shock to a user.
short circuit: is caused by touching of live wires and neutral wire
Fuse: is a protective device used for protecting the circuits from short circuiting and over loading
important diagrams-
1. Magnetic field lines around a bar magnet. 2. Right-hand thumb rule
3. Magnetic field lines through and around a current-carrying solenoid.
4. An electromagnet.
5. A simple electric motor 6. Electric generator
Important activities:
1. Magnetic field lines around a bar magnet
2. Direction of electric current in a simple electric circuit.
3. The direction of Magnetic field lines depends on the direction of electric current.
FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I
Q. PAPER
MARKS-30 TIME- 70 MINUTES
Instructions:
· Questions: 1 to 5 – 1 Mark each · Questions: 6 to 9 – 2 Marks each
· Questions: 10 to 13 – 3 Marks each · Questions 14 – 5 Marks
1. State two uses of electromagnet.
2. An electron moving along X – axis in a magnetic field along Y – axis. In which direction will the electron deflected?
4. What is the importance of earth wire?
5. Should a copper wire be used as a fuse wire? If not, why?
6. Give two points of difference between an electromagnet and a permanent magnet.
7. Draw the lines of force indicating field direction of the magnetic field through and around i) Single loop of wire carrying electric current.
ii) A solenoid carrying electric current.
8. What is a magnetic field? How is the direction of the magnetic field at a point determined?
9. Give four features of domestic electric wiring.
10. Draw a schematic diagram of the domestic wiring system and write its main features.
11. Match the following:
ii) Fleming‘s left-hand rule
a) Force on a conductor in a magnetic field
i) Right hand thumb rule
b) Direction of magnetic field of straight conductor
c) Direction of induced current in conductor
iii) Fleming‘s right-hand rule
d) Polarity of any end of a solenoid.
12. a) Draw a labelled diagram to show how an electro–magnet is made. b) What is the purpose of the soft iron core in making electromagnets?
13. Write two differences between AC and DC current and draw a diagram also.
14. a) Write the principle of an electric generator.
b) Explain the construction and working of the generator. c) Draw a labelled diagram of an electric generator.
HOTS QUESTIONS (SOLVED) 1. On what effect of an electric current does an electromagnet work? A. Magnetic effect of electric current
2. What is the frequency of AC (Alternating Current) in India? A. 50Hz
3. On what effect of an electric current does a fuse work? A. Heating effect of electric current
HOTS QUESTIONS (UNSOLVED) 1. Name the sources of direct current.
2. Why don‘t two magnetic lines intersect each other? 3. What is the role of split ring in an electric motor? 4. What is an earth wire?
ORAL QUESTIONS
1.a) What are magnets?
b) What are natural magnets?
c) What is the meaning of the word lodestone? d) What is the origin of the word magnetism?
2. a) State the law of magnetic poles.
b) What is the surer test of magnetism?
c) What happens if we break a magnet into two pieces? d) Is it possible to obtain isolated north and south poles?
3. a) What is a magnetic line of force?
b) Can two magnetic lines of force intersect? Give reason. c) Magnetic lines of force are endless. Comment.
d) How do the field lines of the regions of strong fields differ from those of weak fields?
4. a) What is a solenoid?
b) Is the magnetic field of a solenoid similar to that of a bar magnet?
c) State the two factors by which the strength of the magnetic field inside a solenoid can be increased.
d) How will you determine the direction of the magnetic field due to a current–carrying solenoid?
5. a) What is an electromagnet?
b) What is the effect of placing an iron core in a solenoid?
c) What type of core should be used inside a solenoid to make an electromagnet? d) Give two advantages of electromagnets.
ORAL QUESTIONS
1. What important observation did Oersted make in his experiments with current-carrying conductors?
2. How can you locate a current–carrying wire concealed in a wall?
3. A freely suspended magnet always points in the north-south direction. Why?
4. What type of core should be used inside a solenoid to make an electromagnet?

GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings